Proton pump. Ion protons proton membrane ions ch25 inside macmillanhighered cations anions Active transport
Pumps (Active Transport) — Definition & Types - Expii
Transport glucose membrane phenomenon involves Pump energy Sodium potassium pump submited images.
New examples of protein pumps
Protein pumpsThe action potential Active transport ( read )Biology: pore protein and carrier protein.
Sodium potassium pump exchange physiology biology muscle human cell function membrane neuron structure choose boardPumps membrane proteins transport types solutes ions three across membranes triangle properties figure other na Sodium-potassium pump which uses atp to pump sodium ions out of theSecondary active transport ( na.

Pump sodium potassium cell membrane transport structure pumps biology biologia proteins molecules diffusion capitulos active resueltas cuestiones protein function cl
Efflux rnd bacteriaWhat is the role of protein channels in the cell membrane? Gonorrhea uses 'pump' to resist antibioticsTransport active pumps antiport example biology types antiporter.
Sodium potassium atp ions hydrolysis adpThe action potential Protein pump transport cell proton active membrane biology cotransport fungi theirFluid biology proteins lipids.

Pumps sodium pump potassium minerals rabbits calcium
Protein transport pore carrier mineral ion absorption channel active membrane biology proteins passive diffusion facilitated ions types simple process gradientPumps (active transport) — definition & types Blog post 8- cell function/structure – izzy powell’s ap bio blog2.4.6 explain the role of protein pumps and atp in active transport.
Proton pumpAtpase pumps The sodium-potassium exchange pumpPumps ca atpase plant class lysosomes.

Channel channels gated membrane cell protein mechanically potential action opening anatomy ion tissue mechanical into when nervous sodium physiology calcium
Transport cell proton pump membrane across gradientAntibiotics bacteria resist certain removes gonorrhea scientists futurity medications allowing Explain ‘fluid mosaic model’ of plasma membrane.Membrane pumps.
Proteins diffusion facilitated membranes molecules polar passive bilayer molecule socratic ion selectiveProtein pumps cell membranes transport mechanisms chapter through ppt movement energy slideserve powerpoint presentation concentration concentrations requiring molecules low into Sodium potassium homeostasis ions science diffusion passive facilitated inside osmosisMembrane cell inositol anatomy bilayer phospholipid channel proteins channels transmembrane potential action types membranes including ion cells phospholipids figure has.


Sodium-Potassium pump which uses ATP to pump sodium ions out of the
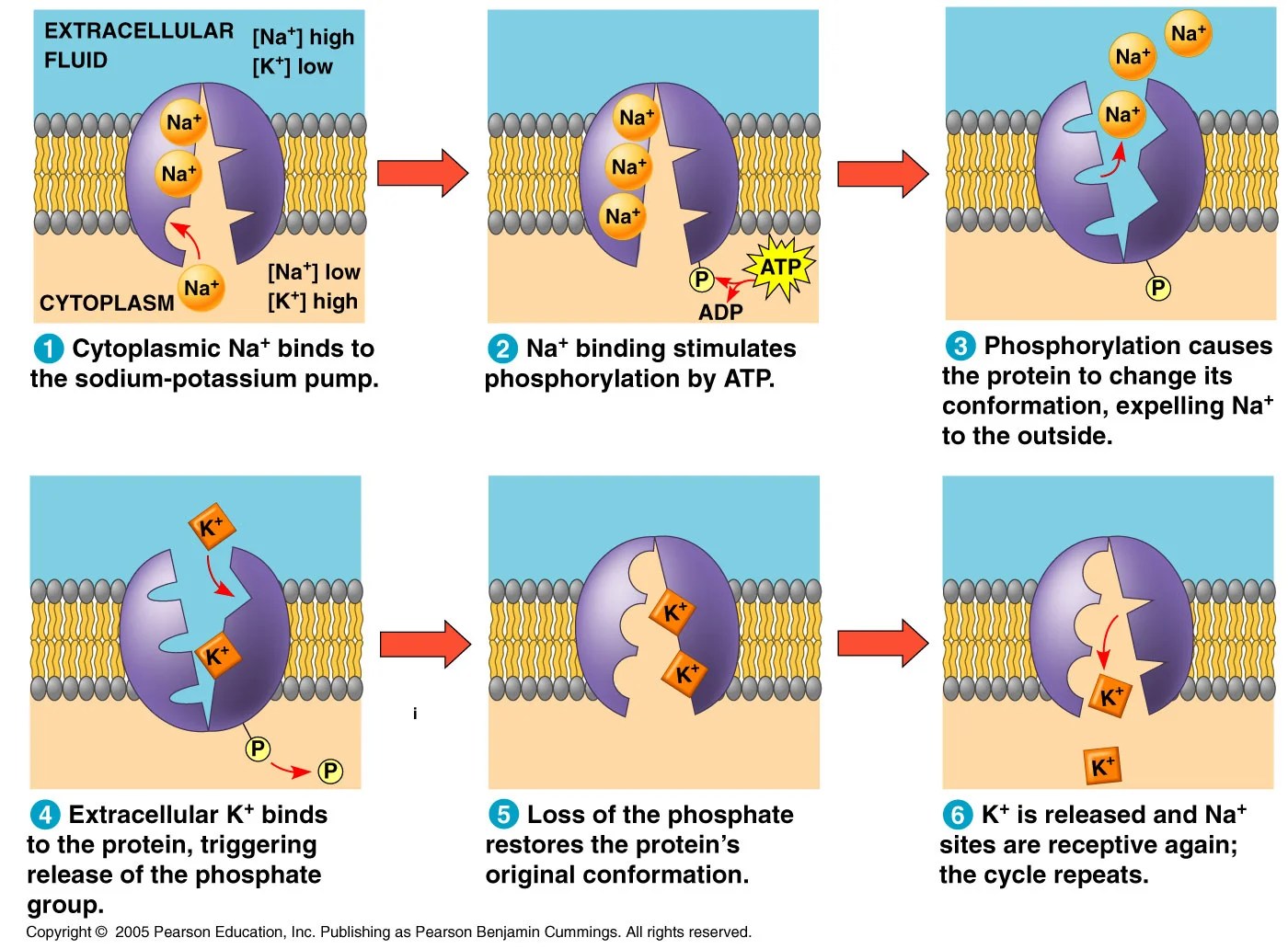
Sodium Potassium Pump submited images.

Secondary Active Transport ( Na - glucose | Class Eleven Chemistry
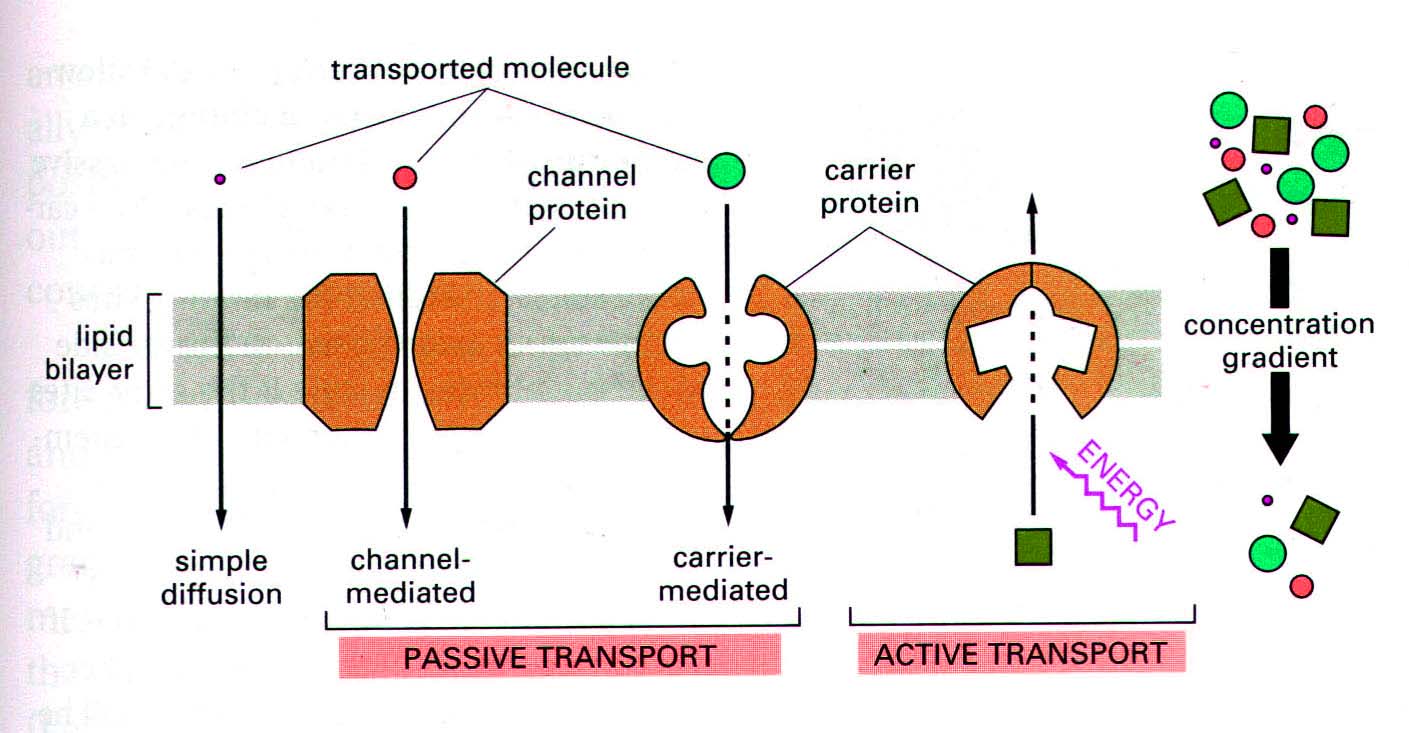
Biology: Pore Protein and Carrier Protein
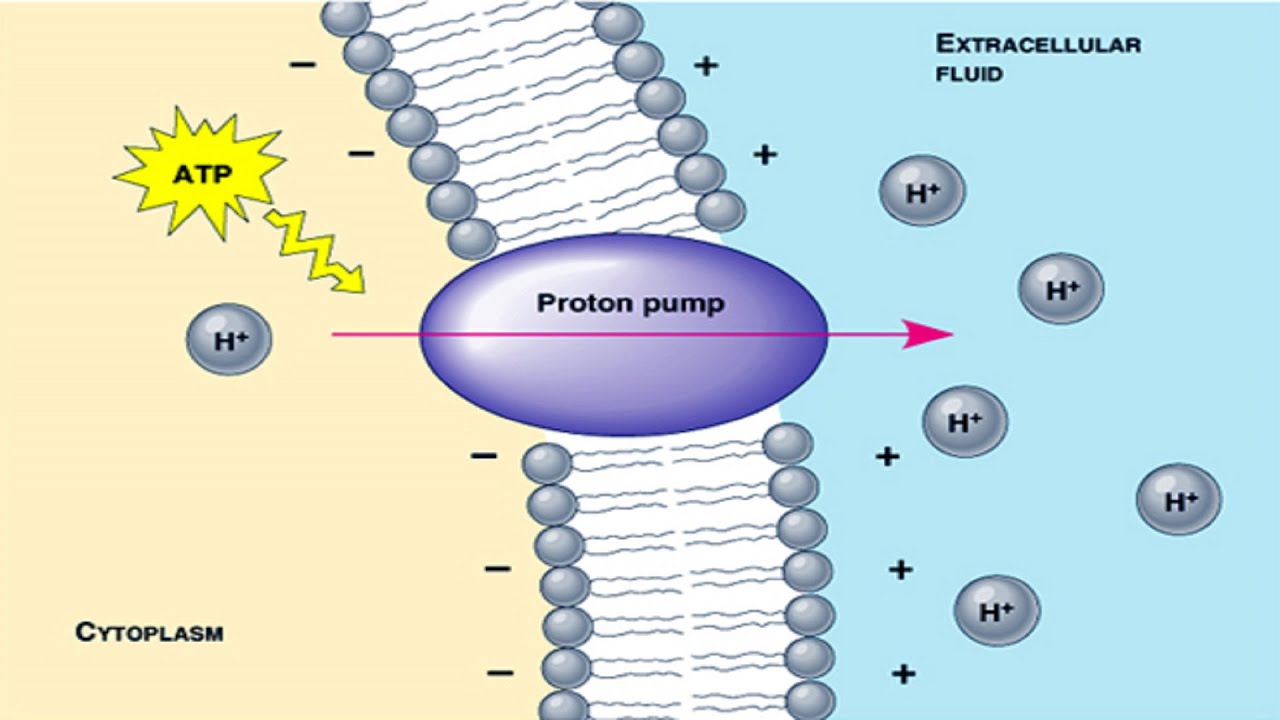
Proton pump. - YouTube

Membrane Pumps | Basicmedical Key

Gonorrhea uses 'pump' to resist antibiotics - Futurity

What is the role of protein channels in the cell membrane? | Socratic